Q:- Define molecular ion. Give examples.
Ans. The chemical species which is formed by a molecule after gaining or losing electrons is called molecular ion. It is unstable so can live for very short time. It can exist at high temperature only.
For example, O21- is the molecular ion of oxygen formed by gaining one electron, O21+ is the molecular ion of oxygen formed by loss of one electron. Similarly, N21- is the molecular ion of nitrogen formed by gaining one electron and N21+ is the molecular ion of nitrogen formed by loss of on electron. Remember that molecular ions cannot form ionic compounds.
Q:- Define free radical. Give examples.
Ans. An atom or group of atoms which has an unpaired electron and no electric charge.
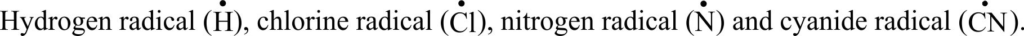
Q:- How is free radical formed? Give example.
Ans. When a molecule, like halogen is exposed to sunlight, it splits into its free radicals. For example,
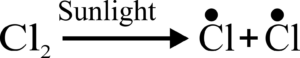
Q:- What are the differences between free radical and an ion? Give examples.
Ans. The following table shows the difference between free radical and ion.
| Free radical | Ion |
| It has an unpaired electron | It has no unpaired electron |
| It carries no electrical charge | It carries electrical charge |
| It has odd number of electrons. For example, chlorine radical (Cl.) has seven electrons. | It has even number of electrons. For example, chloride ion (Cl1-) has eight electrons |
Q:- What are representative particles of a substance? Give examples.
Ans. The particles present in a substance are called its representative particles. For example, H2O molecules are representative particles of water. Similarly, Na atoms are representative particles of sodium element and NaCl formula units are representative particles of sodium chloride.
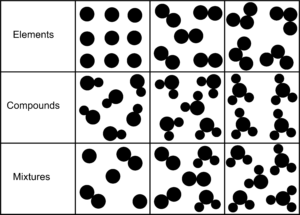
Q:- How to identify an element, compound and mixture. Show diagrams.
Ans. If the particles are formed of same type of atoms, then they are elements. If the particles contain different type of atoms combined then they show compounds. If different type of elements or compounds are mixed, they form mixtures.
The following diagram shows elements, compound and mixtures clearly.
Q:- Define molecule. Differentiate between molecules of elements and compounds . Give examples.
Ans. The particles which can exist freely (independently) is called molecule. Molecules of elements have same types of atoms. For example, He, H2, O3 and S8 are the molecules of helium, hydrogen and sulphur respectively.
On the other hand, the molecules of compounds have different types of atoms. For example, HCl, H2O and C12H22O11 are the molecules of hydrogen chloride, water and sucrose (table sugar) respectively.
Q:- What are monoatomic and polyatomic molecules? Give examples.
Ans. The molecules which consist of one atom only are called monoatomic molecules. For example, He and Ne are monoatomic molecules of helium and neon respectively. All inert gases or noble gases are monoatomic molecules.
On the other hand, the molecules having two or more atoms in them are called polyatomic molecules. For example, H2, CO2 and C6H12O6 are polyatomic molecules of hydrogen, carbondioxide and glucose respectively.
Q:- What is pseudo-science?
Ans. The scientists who worked on changing cheap (less valued) metals such as lead into gold were called Alchemists and that branch was called Alchemy. Alchemy was named pseudo-science (pseudo means false) because Alchemists totally failed in preparing gold from cheap metals.
Q:- What was the importance/advantage of Alchemy?
Ans. Changing cheap metals into gold was wastage of time, but at the same time new processes, like distillation, sublimation and metal extraction were discovered. In this way Alchemists promoted science rather than wasting time.
